On November 5th 2015, two dams of an iron mining reservoir collapsed in Marina, federal state of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Subsequently, a mudslide burst out into Rio Doce, killing at least a dozen people and causing severe damage to nearby villages. The toxic components of the mining wastewaters are likely to harm the ecosystems along Rio Doce. Two weeks after the incident, the polluted waters reached the Brazilian Atlantic Ocean coast.
Using its proprietary, sensor-independent water quality processors, EOMAP was able to track the propagation of the mudslide in Rio Doce on its 650 km journey to the ocean. The arrival of the plume at the estuary was observed in near real time using daily MODIS data – at 500m resolution. The satellite-retrieved turbidity measures provided a good indication on the dynamic impact of the dam collapse.
Higher resolution products, from 30 to 2 m horizontal resolution, are available upon request.

Fig.: Example of 30 m horizontal resolution product (Landsat 7/8, data ©USGS, processing ©EOMAP)
References:
Further reading:
Latest EOMAP News
Reuters bases Mekong article on EOMAP data
WATCOR‑X Bathymetry Software for Navies and Hydrographic Offices
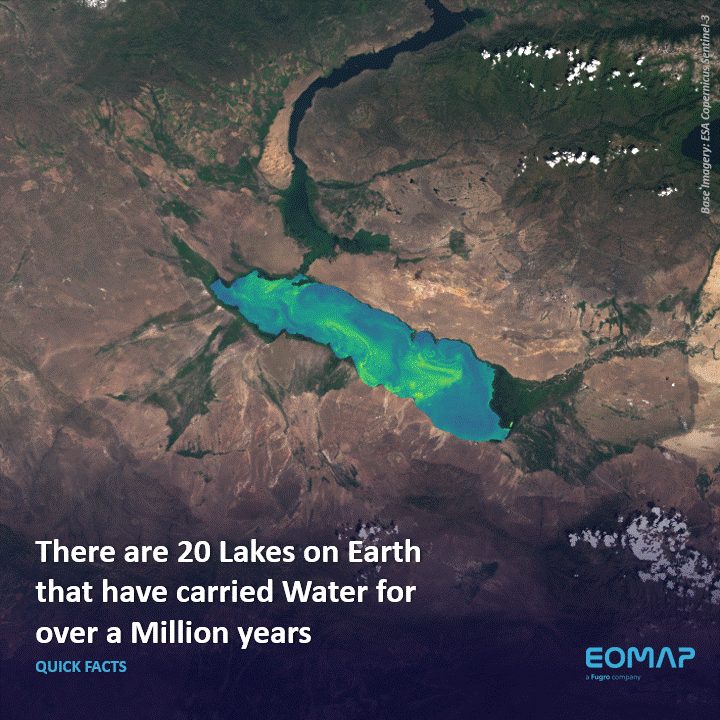
Quick Facts: Ancient Lakes
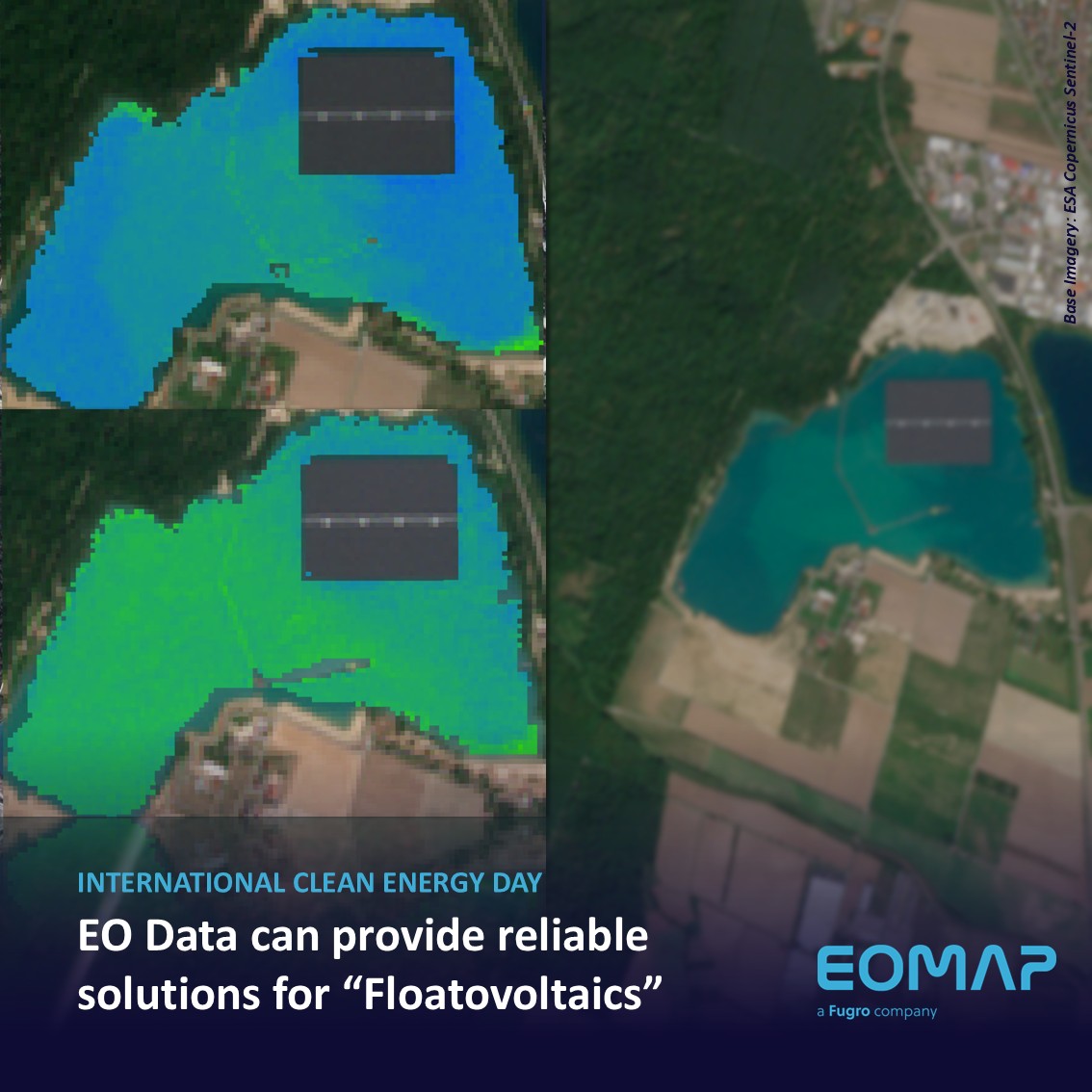
Space-based Intelligence for Clean Energy
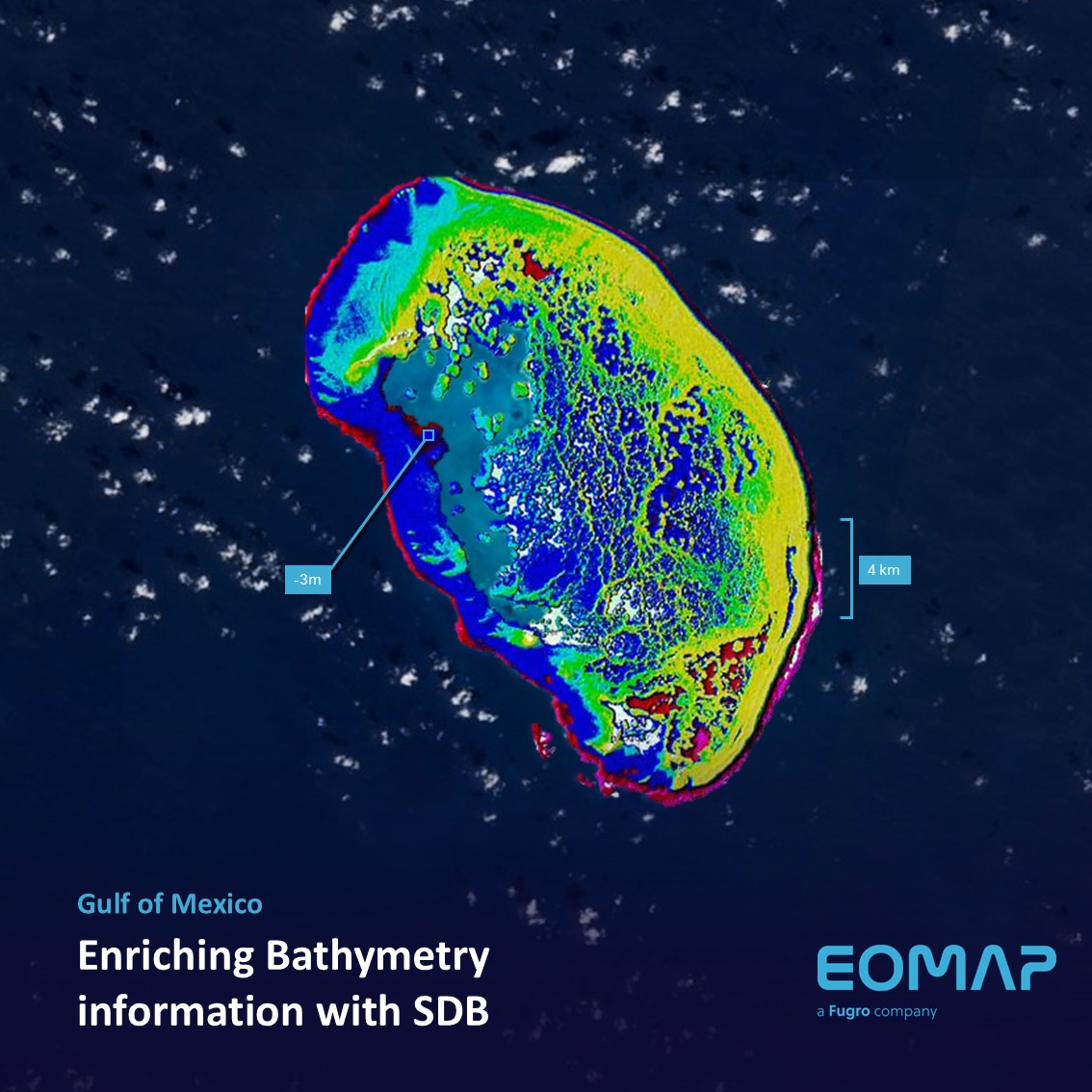
Bathymetry in the Gulf of Mexico
Pro-active hydropower management in winter
Related Posts
02 / 2026
WATCOR‑X Bathymetry Software for Navies and Hydrographic Offices
02 / 2026
Quick Facts: Ancient Lakes
01 / 2026
Space-based Intelligence for Clean Energy
01 / 2026
Bathymetry in the Gulf of Mexico

01 / 2026
Pro-active hydropower management in winter

12 / 2025
From Climate to Nature and Biodiversity: Insights on COP30

12 / 2025
Water Crisis in Iran – Lessons to be learned

11 / 2025
Italian Webinar: Water Quality Monitoring from Space

11 / 2025
Projektstart SEAGUARD

10 / 2025

