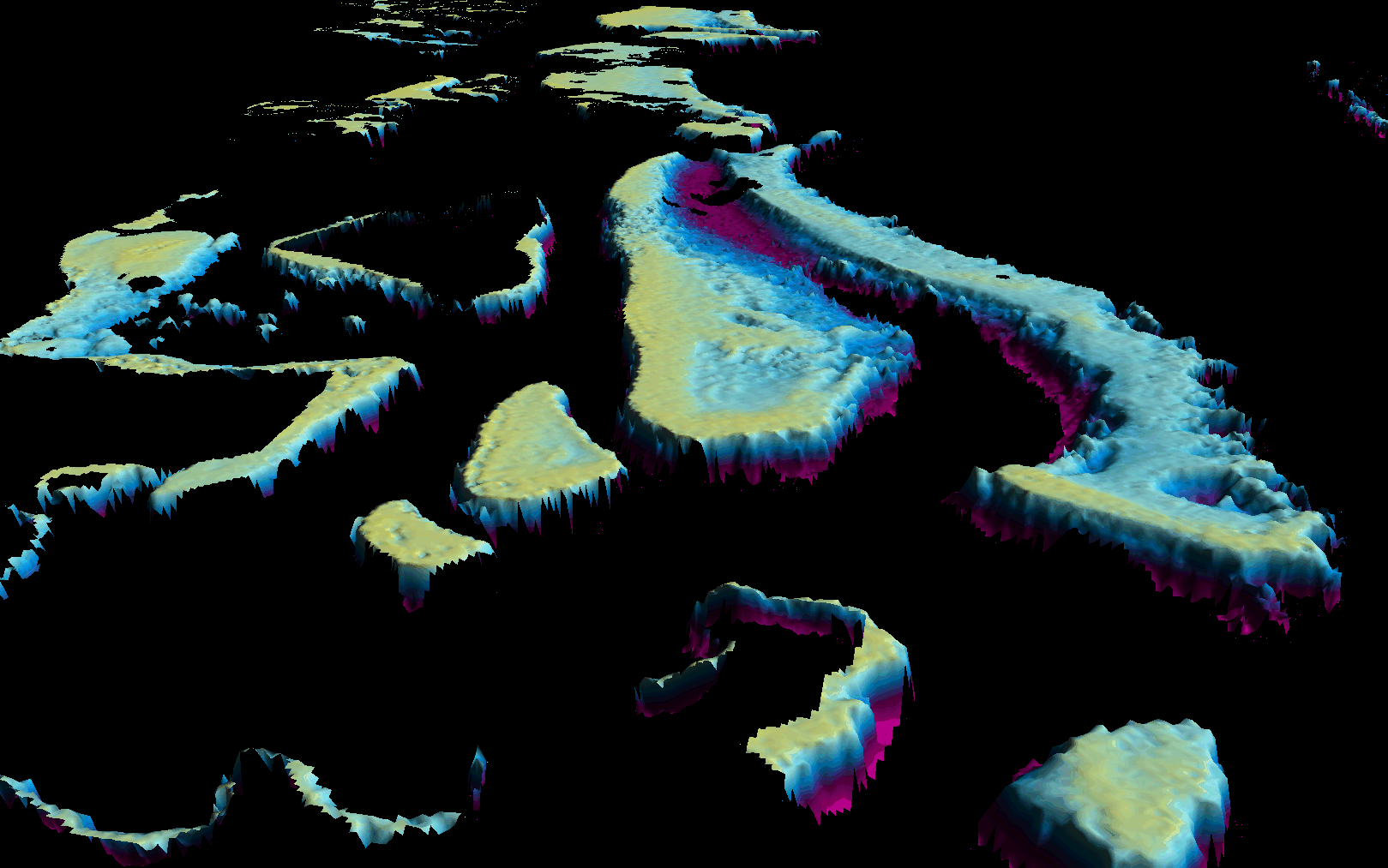
Earth observation (EO) science enthusiasts know how important and complex atmospheric and adjacency correction is for water bodies. For users of EO derivates, such as bathymetry (shown in the figure), water quality parameters, and ocean colour, atmospheric correction routines are key to ensuring standardised and high-quality outputs.
21 European scientists compare key technology
In July 2024, a scientific paper by international scientists from leading research institutions compared MIP (EOMAP’s technology), Polymer, and Acolite. The paper finds “MIP” – used in Germany’s new hyperspectral satellite mission EnMAP – superior.
EOMAP’s atmospheric correction “MIP” inside EnMAP
Hyperspectral remote sensing provides measurements over hundreds of bands from the visible to the infrared. This allows to explore the subtle optical spectral differences, especially in water. Recognising the value of this technology, a new generation of space-borne sensors for terrestrial and aquatic applications has been sent to space, EnMAP is one of them.
Being able to accurately predict water reflectances is one of, if not the most important benchmark of aquatic remote sensing algorithms. Every error in reflectance prediction propagates, thus producing errors in quantities of interest, such as: chlorophyll, turbidity, water depth etc.
The EnMAP standard product is generated by a dedicated water atmospheric correction (AC) called the Modular Inversion Program (MIP), developed by EOMAP physicists.
Intercomparison of 3 atmospheric correction (AC) methods
In the journal “Optics Express”, an international group of scientists from leading research institutions has published the first extensive assessment of the water reflectance products from EnMAP. The 21 geospatial experts evaluated EnMAP’s standard normalized water leaving reflectance over 17 water sites in the first two years of the mission. In this intercomparison exercise between three AC methods – MIP, Polymer and Acolite – MIP showed superior results: MIP-data showed very good agreement between in situ hyperspectral match-ups and EnMAP at the majority of the (17) study sites. And in the conclusion, the scientists find:
The best results were obtained for the MIP AC and demonstrated the robustness of the standard EnMAP [𝜌𝑊]𝑁 products.
By the way: MIP is also “inside” our eoapp series.
More Details
Read the full paper in the journal “Optica”.
Learn more about EnMAP here: https://www.enmap.org/
For more details, please get in touch with EOMAP’s Physics team.
Latest EOMAP News
Reuters bases Mekong article on EOMAP data
WATCOR‑X Bathymetry Software for Navies and Hydrographic Offices
Quick Facts: Ancient Lakes
Space-based Intelligence for Clean Energy
Bathymetry in the Gulf of Mexico
Pro-active hydropower management in winter
Related Posts
02 / 2026
WATCOR‑X Bathymetry Software for Navies and Hydrographic Offices
02 / 2026
Quick Facts: Ancient Lakes
01 / 2026
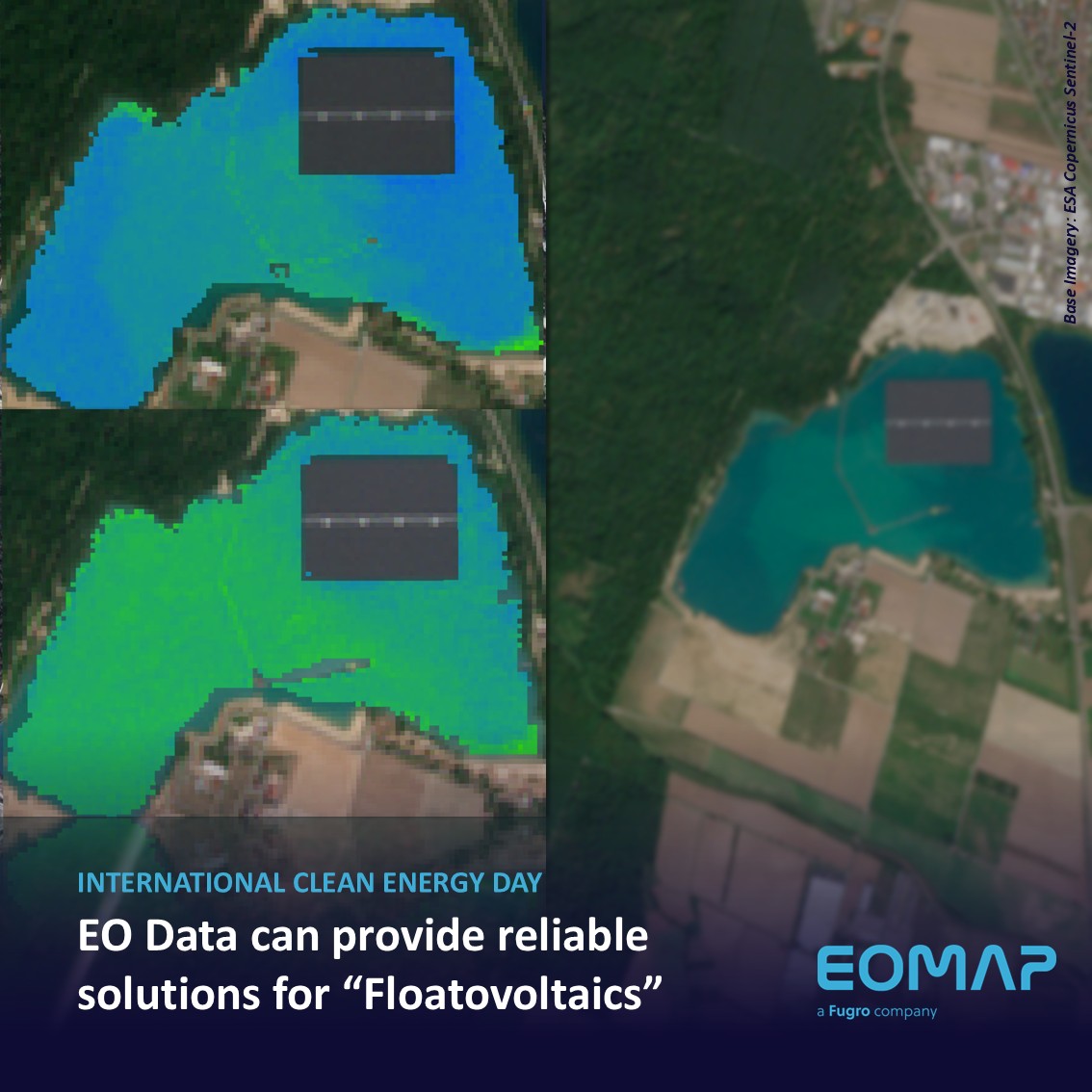
Space-based Intelligence for Clean Energy
01 / 2026
Bathymetry in the Gulf of Mexico

01 / 2026
Pro-active hydropower management in winter

12 / 2025
A short recap of 2025

12 / 2025
From Climate to Nature and Biodiversity: Insights on COP30

12 / 2025
Water Crisis in Iran – Lessons to be learned

11 / 2025
Italian Webinar: Water Quality Monitoring from Space

11 / 2025